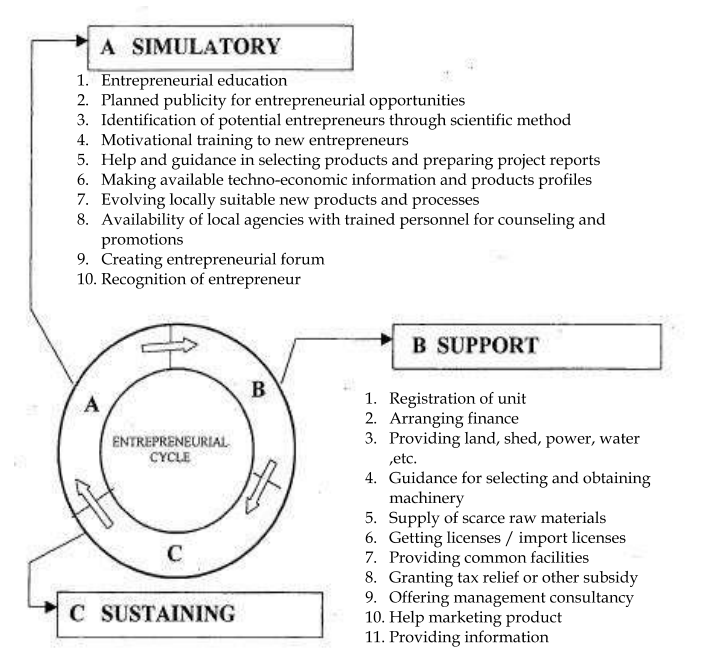
Technological Innovation Management And Entrepreneurship 3rd Module
Meaning of Social Responsibility: Social responsibility is a moral obligation on a company or an individual to take decisions or actions that is in favour and useful to society. Social responsibility in business is commonly known as Corporate Social Responsibility or CSR. For any company, this responsibility indicates that they acknowledge and appreciate the goals of the society, and therefore, would support them to achieve these goals.
Advantages of Social Responsibility
A company can boost its morale and enhance work culture when they can engage their employees with some social causes. There are many factors that can have a positive impact on the business while delivering social responsibilities. Such few factors are
- Justification for existence and growth
- The long-term interest of the firm
- Avoidance of government regulation
- Maintenance of society
- Availability of resources with business
- Converting problems into opportunities
- A better environment for doing business
- Holding business responsible for social problems
Disadvantages of Social Responsibility
Like there are many advantages of social responsibility there are similarly many disadvantages for business. Few factors are mentioned below.
- Violation of profit maximization objective
- Burden on consumers
- Lack of social skills
- Lack of broad public support
Types of Social Responsibilities
Following Are the Different Types of Social Responsibilities:
(1) Economic Responsibility
- Every business is engaged in economic activities.
- So, the prime social responsibility of every business should be economic responsibility.
- Hence they should sell products and service which can satisfy the need of the society.
(2) Legal Responsibility
- The company should comply with the political and legal environment of the country.
- The company should consider protecting the environment.
(3) Ethical Responsibility
- This type of responsibility expects a certain type of behaviour or conduct from the company.
- This behaviour may not be documented by law.
(4) Discretionary Responsibility
- These are voluntary actions taken by the entities in case of natural calamities, helping poor people etc.
- They help them by providing a charitable contribution, education activities etc.
- It prevents investments of charitable funds into speculative activities.
Opinions in Favour of Social Responsibilities:
Following Are the Opinions in Favour of Social Responsibilities:
(1) Justification for Existence and Growth
- Good quality products help in expansion of the business.
- When the business organisation keeps on providing good quality products, it’s actually a fulfillment of social responsibility.
(2) Long Term Interest of the Business
- Every business wants long term profits and gains.
- If increasing no. Of stakeholders are not giving their best, there may be the withdrawal of cooperation of society.
- It can be noted that the public image of the business can be improved by focusing on social goals.
(3) Avoidance of Government Regulations
- Good social behaviour is an ethical aspect of the business. They are beyond the law.
- Business entities avoid government regulations as it their freedom.
(4) Maintenance of Society
- The business should take social responsibilities.
- However, the law is not made for every situation.
- People who are against the organisation can come into conflict. They can also harm the organisation.
- This situation can create criminal intent in society.
(5) Availability of Resources With Business
- Business entities have huge set-ups and good infrastructure.
- These organizations have access to different types of resources.
- These resources should be used for fulfilling social responsibilities.
(6) Holding Business Responsible for Social Problems
- Business activity should see if any type of activity is causing harm to society.
- The business should themselves held responsible for causing harm rather than waiting for any government or social team to come and correct them.
Opinions Which Are Against the Idea of Fulfillment of Social Responsibility:
Following Are the Opinions Against Social Responsibilities:
(1) Violation of Profit Maximisation Objective
- The sole motive of the business is profit maximization.
- Supporting social responsibilities is violating the profit-making objective of the business.
- It would be better if entities increase the profits through increased efficiency.
(2) Burden on Consumers
- Social responsibilities like environment protection, pollution control are very costly in nature.
- If entities opt for these social responsibilities, they always try to shift their burden on ultimate consumers.
- It is not reasonable to charge the customers on the name of social responsibilities.
(3) Lack of Social Skills
- Every entity does not have enough skills and knowledge to solve each and every social problem.
- This can be the reason for a poor image in the society.
- So, these problems should be solved by some specialized parties.
(4) Lack of Broad Public Support
- Generally, society does not accept the involvement of business entities in social programs.
- That is why it gets difficult for the business to solve the problems without the participation of the public.
Social Responsibilities for Different Interest Groups
(1) Responsibility Towards the Shareholders
- Shareholders are the owners of the company.
- The company should make all the efforts to maximize and protect shareholder’s wealth.
- Sharing of useful information with the shareholders, utilization of funds etc.
(2) Responsibility Towards the Workers
- Workers are the key persons behind company success.
- Management of the enterprise must provide the proper working conditions to the workers.
- Workers should get fair salaries and wages.
(3) Responsibility Towards the Consumers
- It is the consumer who buys the company’s product & services.
- So, it is the responsibility of the company to provide the right quality, right quantity with the right price to the consumer.
- There should not be the unfair trade practices like adulteration, poor quality, courtesy to the customers etc.
(4) Responsibility Towards the Government & Community
- Enterprises must follow the laws and regulations of the country/ state in which it is operating.
- The organisation should interact with society to know what they require.
- It should maintain proper infrastructure, proper disposal system and should not cause harm to the society in any manner.
Entrepreneurship:
Definition of Entrepreneur: a person who sets up a business or businesses, taking on financial risks in the hope of profit.
Importance of Entrepreneurship
9 importance of entrepreneurship are;
- Growth of Entrepreneurship.
- Creation of job opportunities.
- Innovation.
- Impact on community development.
- The consequence of business failure.
- Political and economic integration of outsiders.
- Spawns entrepreneurship.
- Enhances the standard of living.
- Promotes research and development.
1. Growth of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship the advent of new venture particularly small ventures to materialize the innovative ideas of the entrepreneurs.
Thus, the growth or establishment of small enterprises ii the specific contribution of entrepreneurship in every economy of the world.
The statistics reveal that in USA economy nearly half a million small enterprise is established every year. Our country is not an exception in this regard.
2. Creation of job opportunities
Entrepreneurship firms contributed a large share of new jobs. It provides entry-level jobs so necessary fur training or gaining experience for unskilled workers.
The small enterprises are the only sector that generates a large portion of total employment every year.
Moreover, entrepreneurial ventures prepare and supply experienced labor to large industries.
3. Innovation
Entrepreneurship is the incubator of innovation. Innovation creates disequilibria in the present state of order.
It goes beyond discovery and does implementation and commercialization, of innovations.
“Leapfrog” innovation, research, and development are being contributed by entrepreneurship.
Thus, entrepreneurship nurses innovation that provides new ventures, products, technology, market, quality of good, etc. to the economy that increases Gross Domestic Products and standard of living of the people.
4. Impact on community development
A community is better off if its employment base is diversified among many small entrepreneurial firms.
It promotes abundant retail facilities, a higher level of homeownership, fewer slums, better, sanitation standards and higher expenditure on education, recreation, and religious activities.
Thus, entrepreneurship leads to more stability and a higher quality of community life.
5. The consequence of business failure
The collapse of the large industry almost has irresistible damage to the development of the state and the state of the economy and the financial condition of the relevant persons.
The incumbents lost their jobs: suppliers and financial institutions face a crisis of recovery.
Customers are deprived of goods, services, and government losses taxes. This could not happen in the case of failure of entrepreneurship.
There shall be no measurable effect upon the economy and no political repercussions too.
6. Political and economic integration of outsiders
Entrepreneurship is the most effective way of integrating those who feel disposed of and alienated into the economy.
Minorities, migrants, and women are safely integrated into entrepreneurship that will help to develop a well-composed plural society.
7. Spawns entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is the nursing ground for new inexperienced adventurists.
It is the field where a person can start his/her idea of the venture, which may be ended up in a giant enterprise. All the large industrial ventures started as a small entrepreneurial enterprise.
Therefore, entrepreneurship provides a wide spectrum of ventures and entrepreneurs in every economy. The vast open arena of entrepreneurship thus acts as an incubator to entrepreneurs.
8. Enhances the standard of living
The standard of living is a concept built on an increase in the amount of consumption of a variety of goods and services over a particular period by a household.
So it depends on the availability of diversified products in the market. Entrepreneurship provides enormous kinds of a product of various natures by their innovation.
Besides, it increases the income of the people who are employed in entrepreneurial enterprises.
That also capable employed persons to consume more goods and services. In effect, entrepreneurship enhances the standard of living of the people of a country.
9. Promotes research and development
Entrepreneurship is innovation and hence the innovated ideas of goods and services have to be tested by experimentation.
Therefore, entrepreneurship provides funds for research and development with universities and research institutions. This promotes the general development, research, and development in the economy.
Entrepreneurship is the pioneering zeal that provides events in our civilization.
We are indebted to it for having prosperity in every arena of human life- economic, technological and cultural.
Concepts of Entrepreneurship
1. Risk Bearing Concept
This is the premier and most popular concept. “entrepreneurship is a function of taking unlimited risks.”
This has revealed that the entrepreneur has to bear various types of risks for establishing the new enterprise and operating it.
These risks are related to time changes and fluctuations in prices.
Entrepreneurship as the concept capacity bear uncertainties. Further, elaborating it they have made a slight differentiation between risk and uncertainty.
According to this, “Uncertainty bear risk, which can neither be predicted nor insured.
The capacity to bear such risks and providing the guarantee against uncertainty is entrepreneurship.
2. Innovative Concept
According to this concept, entrepreneur is a developed economy is that person whose parents something new in the economy.”
Innovation is a specific tool for entrepreneurship.
In this concept, entrepreneurship has been regarded as the adaptation of various innovations in industries, new production systems or techniques, new products, new markets, new marketing methods, new qualities of raw materials, new packaging and new mixture on methods are used.
Hence, this is regarded as a modern entrepreneurship concept.
3. Managerial Skill Concept
The Scholars supporting this concept have turned entrepreneurship as the ability of managerial skills.
Entrepreneurship as the ability for inspections, controls, and direction.
Similarly, entrepreneurship as a Managerial skill, along with the capacity to bear the risks.
4. Creative and Leadership Concept
According to this concept, entrepreneurship as a creative activity and it is the function of progressive leadership.”
Similarly, Entrepreneurship is the quality of developing resources of the institution, developing human capacity, performing creative activities and coordinating new thoughts.
He is of the opinion that new thoughts emerge due to creativity, which may be put to economic use, by efficient leadership.
Creativity activities also expand due to high-level entrepreneurship.
5. High Achievement Capacity Concept
Entrepreneurship is a high achievement capacity concept, for which the capacity of making innovations and taking the decision during risks is essential.
Under the assumption, There is mentioned two characteristics of entrepreneurship:
1. Ability to perform work with the latest method.
2. Ability to take decisions during uncertainties.
Besides, he has also assumed that inspiration for high-level achievements makes a man an entrepreneur.
6. Professional Concept
Modern management experts accept entrepreneurship as a professional concept.
They are of the view that entrepreneurship may be developed through education and training.
Being a managerial ability may be learned by education and training, similarly entrepreneurship attitude maybe also be developed by education and training.
That is why Governments and private organizations conduct various training programs for entrepreneurial ability development.
7. Organisation and Coordination Concept
Entrepreneurship is that economic component that organizes and coordinates various sources of production. Entrepreneurship, as an “ability to organize Enterprise.
8. Business Oriented Concept
Under this concept, entrepreneurship is expressed as the business-oriented entrepreneurial attitude of the individuals, that inspires them to become entrepreneurs, to do the business thinking, to formulate plans and programs and to establish Enterprises.
9. Result Oriented Concept
According to this concept, entrepreneurship is called result-oriented in the modern age.
Now, it is not very important, what efforts have been made for obtaining the goals or how much hard labor has been put, more important is what has been the result?
In the business world, only who succeed in achieving the Goals is recognized as an entrepreneur.
10. Personality, Identity or Role Transformation Process Concept
Entrepreneurship is not only to adopt new works and behavior, but it is also the transformation of personality and to establish a new identity through that.
Characteristics of Successful Entrepreneur
The process of entrepreneurship is a complex one having multidimensional charcterstics. The following are some of the commonly accepted characteristics suggested by experts
1. Curiosity
Successful entrepreneurs have a distinct personality trait that sets them apart from other organizational leaders: a sense of curiosity. An entrepreneur's ability to remain curious allows them to continuously seek new opportunities. Rather than settling for what they think they know, entrepreneurs ask challenging questions and explore different avenues.
This is validated in the online course Entrepreneurship Essentials, where entrepreneurship is described as a “process of discovery." Without curiosity, entrepreneurs can’t achieve their main objective: discovering new opportunities.
The drive they have to continuously ask questions and challenge the status quo can lead them to valuable discoveries easily overlooked by other business professionals.
2. Structured Experimentation
Along with curiosity, entrepreneurs require an understanding of structured experimentation. With each new opportunity, an entrepreneur must run tests to determine if it’s worthwhile to pursue.
For example, if you have an idea for a new product or service that fulfills an underserved demand, you’ll have to ensure customers are willing to pay for it. To do so, you’ll need to conduct thorough market research and run meaningful tests to validate your idea and determine its potential.
3. Adaptability
The nature of business is ever-changing. Entrepreneurship is an iterative process, and new challenges and opportunities present themselves at every turn. It’s nearly impossible to be prepared for every scenario, but successful business leaders must be adaptable. This is especially true for entrepreneurs who need to evaluate situations and remain flexible to ensure their business keeps moving forward, no matter what unexpected changes occur.
4. Decisiveness
To be successful, an entrepreneur has to make difficult decisions and stand by them. As a leader, they’re responsible for guiding the trajectory of their business, including every aspect from funding and strategy to resource allocation.
Being decisive doesn’t always mean being correct. If you want to be an entrepreneur, it means having the confidence to make challenging decisions and see them through to the end. If the outcome turns out to be less than favorable, the decision to take corrective action is just as important.
5. Team Building
A great entrepreneur is aware of their strengths and weaknesses. Rather than letting shortcomings hold them back, they build well-rounded teams that complement their abilities.
In many cases, it’s the entrepreneurial team, rather than an individual, that drives a venture toward success. When starting your own business, it’s critical to surround yourself with teammates who have complementary talents and contribute to a common goal.
6. Risk Tolerance
Entrepreneurship is often associated with risk. While it’s true that launching a venture requires an entrepreneur to take risks, they also need to take steps to minimize it.
While many things can go wrong when launching a new venture, many things can go right. According to Entrepreneurship Essentials, entrepreneurs who actively manage the relationship between risk and reward position their companies to “benefit from the upside.”
Successful entrepreneurs are comfortable with encountering some level of risk to reap the rewards of their efforts; however, their risk tolerance is tightly related to their efforts to mitigate it.
7. Comfortable with Failure
In addition to managing risk and making calculated decisions, entrepreneurship requires a certain level of comfort with failure.
It’s estimated that nearly 75 percent of new startups fail. The reasons for failure are vast and encompass everything from a flawed business model to a lack of focus or motivation. While many of these risks can be avoided, some are inevitable.
Despite this, successful entrepreneurs must prepare themselves for, and be comfortable with, failure. Rather than let fear hold them back, they allow the possibility of success to propel them forward.
8. Persistence
While many successful entrepreneurs are comfortable with the possibility of failing, it doesn’t mean they give up easily. Rather, they see failure as an opportunity to learn and grow.
Throughout the entrepreneurial process, many hypotheses turn out to be wrong, and some ventures fail altogether. Part of what makes an entrepreneur successful is their willingness to learn from mistakes, continue to ask questions, and persist until they reach their goal.
9. Innovation
Many ascribe to the idea that innovation goes hand-in-hand with entrepreneurship. This notion is often true. Some of the most successful startups have taken existing products or services and drastically improved them to meet the changing needs of the market.
Innovation is a characteristic some, but not all, entrepreneurs possess. Fortunately, it’s a type of strategic mindset that can be cultivated. By developing your strategic thinking skills, you can be well-equipped to spot innovative opportunities and position your venture for success.
10. Long-Term Focus
Finally, most people think of entrepreneurship as the process of starting a business. While the early stages of launching a venture are critical to its success, the process doesn’t end once the business is operational.
According to Entrepreneurship Essentials, “it’s easy to start a business, but hard to grow a sustainable and substantial one. Some of the greatest opportunities in history were discovered well after a venture launched.”
Entrepreneurship is a long-term endeavor, and entrepreneurs must focus on the process from beginning to end to ensure long-term success.
Different types of entrepreneur
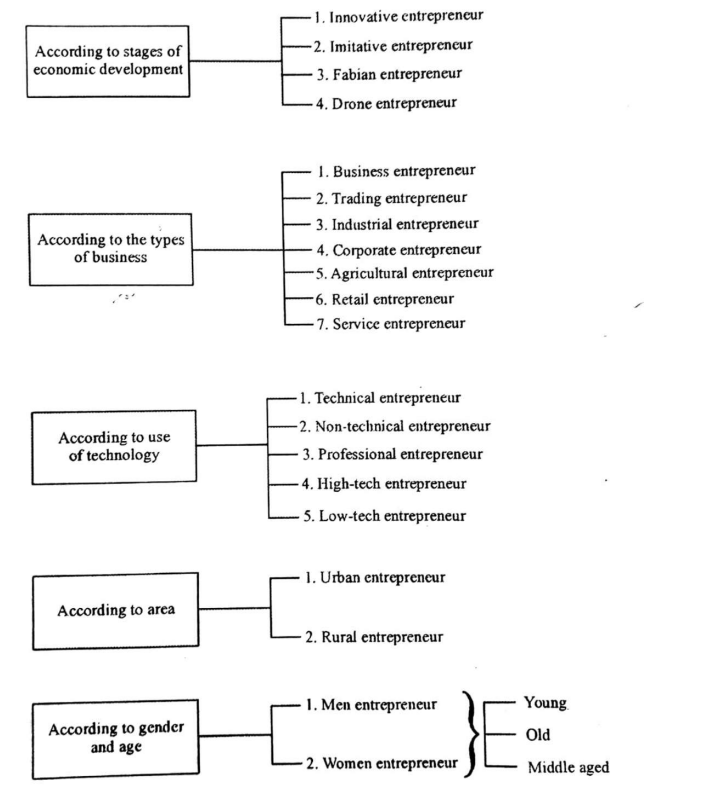
According to stages of economic development
1. INNOVATIVE ENTREPRENEUR
An innovative entrepreneur is one who introduces new product, new service or new market. An innovative entrepreneur is also known as modern entrepreneur. An innovative entrepreneur can work only when a certain level of development is reached. These entrepreneurs introduce new changes and develop the business after a certain level of development is reached. They invent new products. Such kind of entrepreneurs can be seen in developed countries, as large sum of money can be diverted towards research and development purposes.
2. ADAPTIVE ENTREPRENEUR
Adaptive entrepreneur is one who adopts the successful innovations of innovative entrepreneur. These entrepreneurs imitate the techniques and technologies innovated by others. These entrepreneurs can be seen both in underdeveloped and developing countries. They also make small changes in relevance to their market environment.
3. FABIAN ENTREPRENEUR
A fabian entrepreneur is one who responds to changes only when he is very clear that failure to respond to changes would result in losses. Such entrepreneurs do not introduce new changes. They also do not desire to adopt new methods. They are very shy and stick to old customs. They are very cautious.
4. DRONE ENTREPRENEURS
These entrepreneurs do not make any changes. They refuse to utilize the opportunities and may also suffer losses. They are very conventional. They refuse to introduce changes. They even make losses but avoid changes. Sometimes they may be pushed out of the market.
According to type of business
1. BUSINESS ENTREPRENEURS
Business entrepreneurs we those who conceive an idea to for a new product or service and then create a business to convert their ideas into reality. These entrepreneurs may be found in small business units or big enterprises. They concentrate both on production and marketing activities. Example: A Printing Press, bakery or a textile unit.
2. TRADING ENTREPRENEURS
Trading Entrepreneurs are those who undertake trading activities. These entrepreneurs do not concentrate on manufacturing activities. They give more emphasis on distribution and marketing of goods. They identify potential markets, create demand for the product and influence people to buy the product. Example: Agents and Wholesalers.
3. INDUSTRIAL ENTREPRENEURS
Industrial Entrepreneurs are those who concentrate in industrial and production activities. Trey identify the needs of the customers and manufacture a product according to their needs. They are generally a product-Oriented entrepreneur. Example: A manufacturer of Automobile spare parts, computer accessories.
4. CORPORATE ENTREPRENEUR
Corporate entrepreneurs are those who exhibit innovative skills in organizing and managing corporate undertaking. Example: A Trust registered under the Trust Act.
5. AGRICULTURAL ENTREPRENEUR
An agricultural entrepreneur is one who concentrates on agricultural activities. These entrepreneurs concentrate on activities like raising agricultural production, marketing of fertilizers etc.
6. RETAIL ENTREPRENEURS
Retail entrepreneurs are those who undertake trading activities. They have direct contact with customers and hence they are customer oriented. Example: An entrepreneur running a departmental store
7. SOCIAL ENTREPRENEUR
A social entrepreneur is one who provides importance to the society by serving them. He concentrates on social issues and does not aim to make profit. Example: A person running an orphanage.
ACCORDING TO TECHNOLOGICAL ASPECTS
According to Technical Aspects, Entrepreneurs shall be classified as Technical Entrepreneurs, Non-Technical Entrepreneurs and Professional Entrepreneurs.
1. TECHNICAL ENTREPRENEUR
A technical entrepreneur is one who concentrates more on production activities. He has got sound technical knowledge. He utilizes his technical knowledge and demonstrates his innovative capabilities. He is also known as technocrat.
2. NON-TECHNICAL ENTREPRENEUR
A non-technical entrepreneur concentrates more on marketing activities. He tries to find out new strategies for marketing goods. He also promotes his business by employing various marketing methods.
3. PROFESSIONAL ENTREPRENEUR
Professional entrepreneur is a person who applies innovative ideas in setting up of a business. He is interested in establishing the enterprises rather than managing it. Once the business is established. the entrepreneur will sell the business to some one else.
Myths of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is a career which is gaining popularity worldwide but still isn’t very well understood which is why there are so many myths regardion these career option. A lot of people believe these myths to be true which is why they don’t pursue their ambition of being an entrepreneur despite having a great idea
1. Entrepreneurs are born, not made. This is the most common myth that deters people from becoming entrepreneurs. However this is completely untrue. A normal person with an idea which solves a problem the society is dealing with can become an entrepreneur if he works on certain skills. If one is ready to develop on leadership and managerial skills and isn’t scared to take risks, one can aim to become a successful entrepreneur.
2.All you need is money. This myth is not completely justified because you may have great investors pumping in a lot of money into your venture but if you’re idea doesn’t appeal to the people they will not buy your product or service. Thus, money might be important but it is more important to use the money wisely in places where it is required.
3. Entrepreneurs are usually college drop-outs.
This is a common disbelieve because great people like Mark Zuckerberg, Mukesh Ambani and Steve Jobs have managed to become successful entrepreneurs without a college degree. However, a formal and educated background only helps an entrepreneur to understand concepts and the business better. An entrepreneur becomes one of his idea and developed skills set and not college degree
4. You need an out of the box idea to start up
This is another myth about entrepreneurship which needs to be debunked. It is true that you need an idea to develop on but the idea doesn't need to be completely new or innovative one. Running a restaurant, school or any kind of business or adding value to an already existing idea which solves problems of the society can also serve a great base for entrepreneurship
5. Having no boss is the best feeling
A lot of people consider entrepreneurship because they believe they will get to set their own terms at work and lead a team. However, this might not be a favorable scenario for every venture. With ideas like leadership coaches coaching up, it is proved that even entrepreneurs who lead a team require help from superiors in order to succeed.
6.You need the perfect timing
People often comment saying that it is actually luck which will make you a successful entrepreneur. They believe that it is important that the time is right and destiny is in your favour. However, the history of entrepreneurs has proved this to be absolute rubbish as successful people like Reid Hoffman, the founder of LinkedIn, got success only later in his life